1162Structural reinforcement of O/W bigels by incorporating soy protein isolate–gellan gum complex and beeswax: Enhancing 3D printing precision and freeze-thaw stability
1Dept. of Biotechnology, College of Life Science and Biotechnology, Korea University, 145, Anam-ro, Seongbuk-gu, Seoul 02841, Republic of Korea
2Dept. of Food Bioscience and Technology, College of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, Korea University, 145, Anam-ro, Seongbuk-gu, Seoul 02841, Republic of Korea
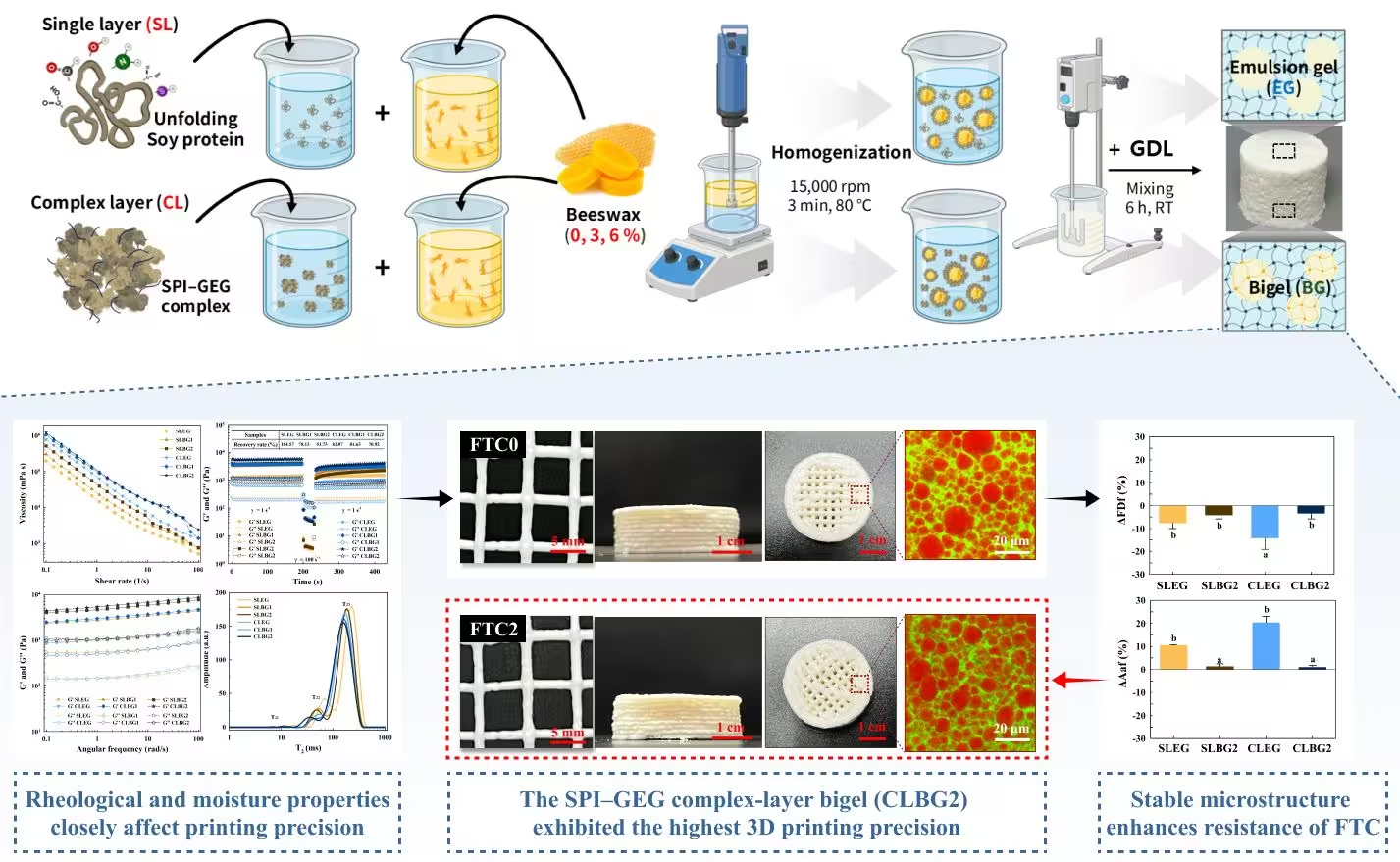
This study presents a novel strategy to enhance the freeze-thaw stability and printability of clean-label food inks by developing a complex-layer bigel (CLBG) system. In this system, soy protein isolate (SPI) and gellan gum (GEG) were used to form a complex to structure the aqueous phase, while beeswax (BW) was added to structure the oil phase through crystallization. A systematic comparative analysis between single-layer and complex-layer systems revealed that the complex-layer system, formed by electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonding between SPI and GEG, established a robust interfacial network. This significantly improved viscoelastic properties compared to the single-layer system stabilized solely by protein. In addition, the conversion of free water into bound water was confirmed to greatly enhance the structural stability of the gel system. Notably, the dual-structuring strategy, combining aqueous phase structuring through the complex and oil phase structuring through the incorporation of beeswax (BW), further strengthened structural integrity through synergistic effects. This effectively mitigated structural damage caused by ice crystal formation during freezing, enabling the ink to stably maintain its inherent viscoelastic properties, water- and oil-holding capacities, and ζ-potential even after thawing. Consequently, color changes were suppressed to a level imperceptible to the naked eye (Δ E* < 3), despite undergoing freeze-thaw cycles. Furthermore, this system demonstrated outstanding 3D printing performance with high shape fidelity and deposition precision. Overall, the dual-structuring strategy integrating SPI-GEG complexes and wax presents a promising approach for designing freeze-thaw stable matrices for fat replacers in frozen foods and functional 3D printing applications.